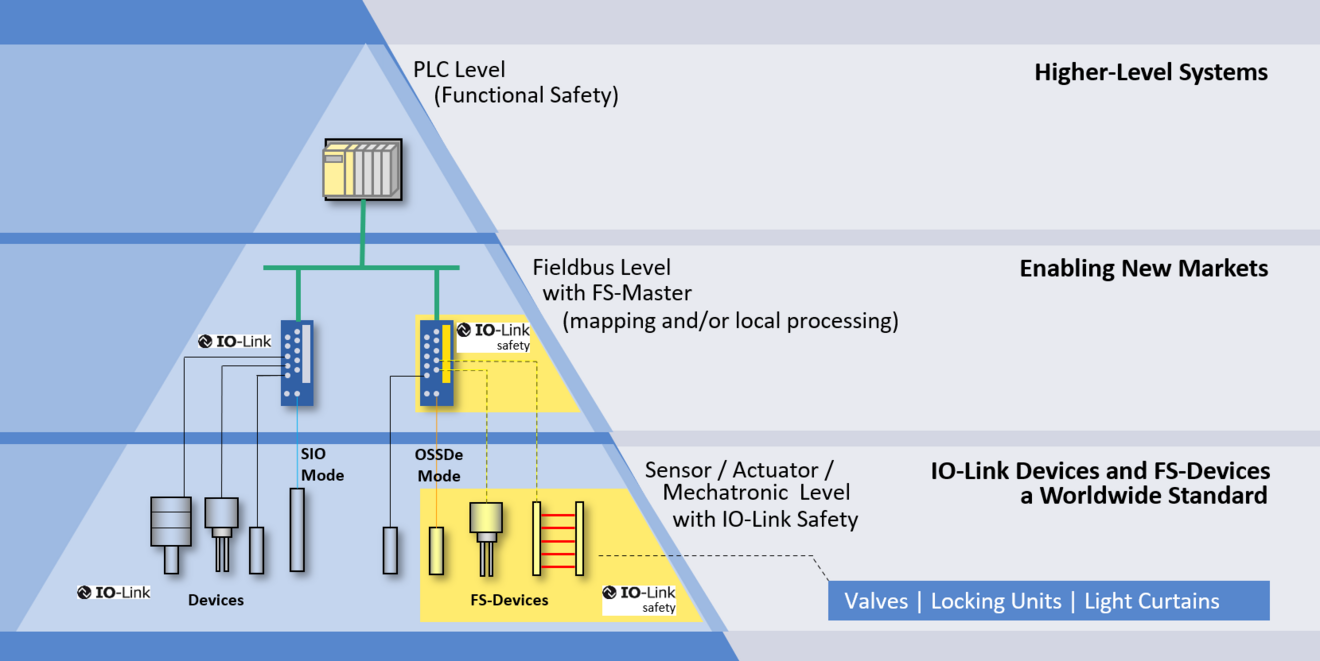
IO-Link Safety uses IO-Link as a so-called black channel to transmit safety-related data. IO-Link Safety therefore initially offers all the advantages of IO-Link. IO-Link Safety allows for the reliable implementation of devices and applications with up to SIL 3. The worldwide distribution is supported by standardization as IEC 61139-2.
The functional safety communication protocol is specially designed for IO-Link and its point-to-point communication and is therefore simpler than the corresponding safety protocols for fieldbus systems. The IO-Link Safety Masters then take over the implementation in the higher-level systems.
The ports of IO-Link Safety Masters can always be configured for IO-Link. This makes mixed applications with standard functionality and functional safety easier and more cost-effective to implement.
For the migration from conventional technology to IO-Link Safety, IO-Link Safety Masters can offer ports that can be configured for the connection of OSSD sensors.
Similar to the SIO mode with IO-Link, manufacturers can also offer IO-Link Safety Devices that can be operated in conventional applications with OSSD as well as in new applications with IO-Link Safety. This promotes the rapid emergence of a wide range of products.
Like IO-Link Link, IO-Link Safety is equally suitable for sensors, actuators and mechatronic components. Safety-related and standard data can be transmitted at the same time. This so-called mix mode makes IO-Link Safety very powerful and applicable to complex devices such as drives.
Due to the much greater effort required for development and approval compared to standard devices, it is even more important for manufacturers not to have to implement different communication protocols and connections in their safety-related devices.
This not only benefits the manufacturers, but also makes many developments possible and promotes product diversity.
The IODD is used for parameterization and integration in applications. The standards for functional safety require a tool that is permanently assigned and approved for the respective device for parameterizing safety functions.
In addition to the IODD, there is therefore also a so-called "Dedicated Device Tool" for the IO-Link Safety Device. To ensure that this can also be used in all systems, there is a standardized software interface DTI (Device Tool Interface).